Definition of Irrigation: Irrigation is the artificial means of supplying water to plants for its growth and maturity
Necessity of Irrigation:
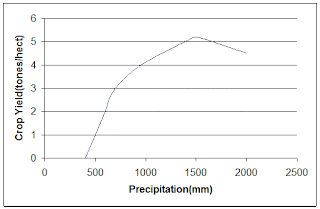
1. Rainfall < water requirement for plants
2. Rainfall is sufficient but the spatial distribution is not as per requirement
3. Rainfall is sufficient, the spatial distribution is also good but the temporal distribution is not as per requirement
4. Advanced scientific development, such as use of fertilizer, insecticide etc.
Objectives of Irrigation:
1. Ensure enough moisture essential for plant growth
2. Provide crop insurance against short duration of drought
3. Cool the soil and atmosphere to provide a suitable surrounding
4. Wash out / dilute harmful salts, chemical in the soil
5. Reduce hazards of soil piping
6. Soften the tillage pan
Advantage of Irrigation:
1. Increase of food production
Multiple cropping
Growing high yielding varieties
Timely agricultural operation
Control of weed
2. Modify soil or climate environment – leaching
3. Elimination of mix cropping
4. Lessen risk of catastrophic damage caused by drought
5. Increase income/national cash flow
6. Increase labor employment
7. Increase standard of living
8. Increase value of land
9. Domestic and industrial water supply
10. Improve communication and navigation facilities
11. Improvement in the ground water storage
12. Development of recreation facilities
13. Improve fish culture
14. Generation of hydro-electric power
Disadvantage of Irrigation:
1. Water logging
2. Ill aeration of soil
3. Pollution of under ground water
4. Result in colder and damp climate causing diseases like malaria
Social and environment aspects of irrigation
Agriculture is the largest sector of the Bangladesh economy
The largest source of employment
Of 17 million rural households, 11 million are engaged in farming
Two types: small holding farmers and medium-holding farmers
Constraints to productivity and expansion of irrigation among small holders include lack of access to cheap credit, low incentive to invest in inputs and irrigation, insecurity of crops, lack of knowledge etc.
Require good attention to low interest credit and information packages.
Main environmental issue is the effects on ponds and stream flows in dry season.
Use of fertilizer deteriorates water quality
Some research shows that arsenic problem may also related with the ground water irrigation
Irrigation structures reduce fish migration of the river system. Some fish friendly structures reduce this problem. Example: Pilot Fish-pass project connecting the Manu River and Kawadighi Haor in North East Region.